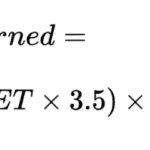Sleep Quality Calculator: Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index
Getting a good night’s sleep is essential for maintaining physical health, emotional well-being, and mental clarity. In a world full of hustle and bustle, understanding your sleep quality can help you make informed decisions to improve your rest. The Sleep Quality Calculator offers a fun and creative way to evaluate your sleep patterns and help you wake up feeling refreshed.
Sleep Quality Calculator

Get our Free App to track Sleep, Calories, Workouts and more!
We have both Epworth sleepiness scale score, Pittsburgh sleep index for you to determine you REM sleep. Don't just track your sleep but you can also track workouts, calories, periods, medication and much more for FREE!
What is the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI)?
The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) is a widely used self-report questionnaire designed to assess sleep quality and disturbances over a one-month period. It evaluates multiple aspects of sleep, including duration, disturbances, latency (time taken to fall asleep), and overall sleep efficiency. The PSQI is commonly used in clinical and research settings to identify poor sleep quality and potential sleep disorders such as insomnia, sleep apnea, and circadian rhythm disorders.
Components of the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI)
| Component | What It Measures |
|---|---|
| Sleep Duration | Total hours of sleep per night |
| Sleep Latency | Time taken to fall asleep |
| Sleep Efficiency | Ratio of actual sleep time to time spent in bed |
| Sleep Disturbances | Frequency of disruptions (e.g., waking up at night) |
| Sleep Quality | Subjective assessment of overall sleep quality |
| Use of Sleep Medication | Frequency of medication use to aid sleep |
| Daytime Dysfunction | Impact of poor sleep on daily activities (e.g., fatigue, concentration issues) |
Each component is scored from 0 to 3, and the total PSQI score ranges from 0 to 21, with higher scores indicating poorer sleep quality.

Understanding
What the Pittsburgh Sleep questionnaire?
The PSQI consists of 19 self-rated questions and 5 additional questions for a bed partner or roommate (optional). These questions are grouped into 7 components, each scored from 0 (no difficulty) to 3 (severe difficulty). Each element is scored from 0 to 3, and the total PSQI score ranges from 0 to 21, with higher scores indicating poorer sleep quality. Refer university website here
Free Download PSQI questionnaire PDF

sleep deeper
How to Get More REM Sleep: Improve Sleep Quality
Getting sufficient REM sleep is crucial for cognitive function, emotional regulation, and overall well-being. This deep stage of sleep enhances memory, learning, and brain processing. If you're struggling with poor sleep quality or low REM sleep, here’s how to improve it.
what does rem stand for?
REM stands for Rapid Eye Movement sleep which is the deepest stage of sleep where dreams occur, and the brain is highly active. It plays a key role in memory consolidation, emotional processing, and creativity. Your sleep cycle typically includes 4–6 REM sleep periods, with the longest occurring in the final hours of sleep.
How to Increase REM Sleep
- Maintain a Consistent Sleep Schedule
- Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends.
- Irregular sleep patterns can disrupt REM cycles.
- Optimize Your Sleep Environment
- Keep your bedroom dark, cool (60-67°F or 15-19°C), and quiet.
- Use blackout curtains, white noise machines, or sleep masks if needed.
- Avoid Alcohol and Caffeine Before Bed
- Get Enough Total Sleep
- REM sleep occurs in later sleep cycles, so sleeping at least 7–9 hours is essential.
- Short sleep durations reduce overall REM sleep.
- Reduce Stress and Anxiety
- High stress levels can disrupt sleep cycles and reduce REM sleep.
- Try meditation, deep breathing, or progressive muscle relaxation before bed.
- Exercise Regularly
- Moderate exercise (e.g., walking, yoga, strength training) improves sleep quality.
- Avoid high-intensity workouts right before bedtime, as they may delay sleep onset.
- Manage Light Exposure
- Morning sunlight exposure helps regulate your circadian rhythm.
- Avoid blue light (from screens) at least 60–90 minutes before bed.
- Use blue light filters or night mode on your devices.
- Eat REM-Boosting Foods
- Foods rich in magnesium, tryptophan, and melatonin can enhance REM sleep:
- Bananas, almonds, walnuts (magnesium)
- Turkey, eggs, dairy (tryptophan)
- Cherries, kiwi, oats (melatonin)
- Foods rich in magnesium, tryptophan, and melatonin can enhance REM sleep:
- Consider Taking a Power Nap
- Short naps (20–30 min) can boost energy but avoid long naps that enter deep REM sleep.
- Use Sleep Tracking Tools
- Apps or wearable devices (like Fitbit, Oura Ring) help monitor your REM sleep percentage.
- If sleep issues persist, consult a sleep specialist for a detailed evaluation.

What is the Epworth Sleepiness Scale?
The Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS) is a self-administered questionnaire designed to measure a person's level of daytime sleepiness. It helps assess the likelihood of falling asleep in various daily situations and is commonly used in diagnosing sleep disorders such as sleep apnea, narcolepsy, and insomnia.
Key Differences: Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS) vs. Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI)
| Factor | Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS) | Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) |
|---|---|---|
| Measures | Daytime sleepiness | Overall sleep quality |
| Focus | Likelihood of falling asleep in different situations | Sleep habits, duration, and disturbances |
| Scoring Range | 0–24 | 0–21 |
| Usage | Identifies excessive daytime sleepiness | Evaluates long-term sleep patterns |
| Common Uses | Sleep apnea, narcolepsy screening | Insomnia, poor sleep quality assessment |
The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) is a comprehensive tool for measuring long-term sleep quality, while the Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS) focuses on daytime drowsiness. If you experience poor sleep or daytime fatigue, these tools can help assess your sleep health and guide further evaluation.

why is rest important
Stages of Sleep in Psychology: Understanding the Sleep Cycle
The Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS) is a self-administered questionnaire designed to measure a person's level of daytime sleepiness. It helps assess the likelihood of falling asleep in various daily situations and is commonly used in diagnosing sleep disorders such as sleep apnea, narcolepsy, and insomnia.
Understanding the Sleep Cycle
- A full sleep cycle lasts about 90–110 minutes and repeats 4–6 times per night.
- The first half of the night has more deep sleep (Stage 3).
- The second half of the night has longer REM sleep periods.
Typical Sleep Cycle Progression:
Stage 1 → Stage 2 → Stage 3 → Stage 2 → REM Sleep → Repeat
| Stage | Duration | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
| NREM 1 | 1–7 min | Light sleep, transition from wakefulness |
| NREM 2 | 10–25 min | Memory processing, reduced awareness |
| NREM 3 | 20–40 min | Deep sleep, physical repair |
| REM | 10–60 min | Dreaming, emotional processing |
Why Are Sleep Stages Important?
- Disruptions in sleep stages can lead to memory problems, mood disorders, and weakened immunity.
- Lack of deep sleep causes fatigue and poor physical recovery. (Find your stress levels here)
- Lack of REM sleep affects emotional health, creativity, and decision-making.

relation with food and nutrition
The Connection Between Sleep, Food, and Nutrition
Sleep and nutrition are deeply interconnected. What you eat affects sleep quality, duration, and sleep cycle stages, while poor sleep can impact hunger hormones, metabolism, and nutrient absorption. Understanding this relationship can help improve both sleep health and overall well-being.
How Food Affects Sleep
1. Nutrients That Support Better Sleep
Certain vitamins and minerals play a key role in sleep regulation:
| Nutrient | How It Helps Sleep | Food Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Magnesium | Promotes relaxation and melatonin production | Almonds, spinach, bananas |
| Tryptophan | Amino acid that helps produce serotonin and melatonin | Turkey, eggs, dairy, seeds |
| Melatonin | Regulates the sleep-wake cycle | Tart cherries, kiwi, walnuts |
| Calcium | Supports melatonin production | Dairy, leafy greens, sardines |
| Zinc | Aids sleep stability and REM sleep | Pumpkin seeds, chickpeas, cashews |
| B Vitamins | Helps regulate serotonin and reduce stress | Whole grains, meat, legumes |
2. Vitamin D and Sleep: The Sunshine Connection
- Vitamin D deficiency is linked to poor sleep quality, insomnia, and increased daytime fatigue.
- Low vitamin D levels can reduce deep sleep (Stage 3) and REM sleep, leading to lighter, fragmented sleep.
- Sources of Vitamin D:
- Sunlight exposure (15–30 minutes per day)
- Foods: Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), fortified dairy, eggs
- Supplements if levels are clinically low
👉 Tip: If you struggle with sleep issues, check your vitamin D levels and consider safe sun exposure or diet adjustments.
Foods That Promote Better Sleep
Eating the right foods before bed can enhance sleep quality by increasing melatonin and relaxation.
Best Foods for Sleep:
- Tart Cherries – High in natural melatonin to improve sleep onset.
- Kiwi – Rich in antioxidants and serotonin, enhances REM sleep.
- Bananas – Contains magnesium and potassium, relaxes muscles.
- Walnuts & Almonds – Provide melatonin, magnesium, and healthy fats.
- Warm Milk & Yogurt – Rich in calcium and tryptophan, helps melatonin production.
- Oatmeal – Whole grains increase serotonin levels, reducing stress.
- Turkey – Contains tryptophan, a precursor to serotonin and melatonin.
👉 Tip: Eat a light snack (not a heavy meal) 30–60 minutes before bedtime to avoid digestion issues.
Foods That Disrupt Sleep
Certain foods can reduce sleep quality by affecting melatonin, digestion, or alertness.
Worst Foods for Sleep:
- Caffeine (Coffee, Tea, Soda, Chocolate) – Blocks adenosine (sleep-promoting hormone).
- Alcohol – Disrupts REM sleep and causes frequent awakenings.
- Spicy & Acidic Foods – Can cause heartburn and indigestion.
- High-Sugar Foods (Candy, Pastries, Processed Foods) – Spikes blood sugar, causing energy crashes.
- Heavy & Fatty Meals (Fried Foods, Fast Food, Red Meat) – Slows digestion and raises body temperature.
👉 Tip: Avoid caffeine and high-fat foods at least 6 hours before bedtime for better sleep.